Unveiling the Thyroid’s Vital Role: Understanding Its Function
The thyroid, a small but mighty gland located at the base of your neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating numerous bodily functions. Understanding cuál es la función de la tiroides, or what the function of the thyroid is, is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. This butterfly-shaped gland secretes hormones that influence metabolism, growth, and development. A malfunctioning thyroid can lead to a cascade of health issues, underscoring the importance of comprehending its function and maintaining its optimal performance.
The Thyroid Gland: An Overview
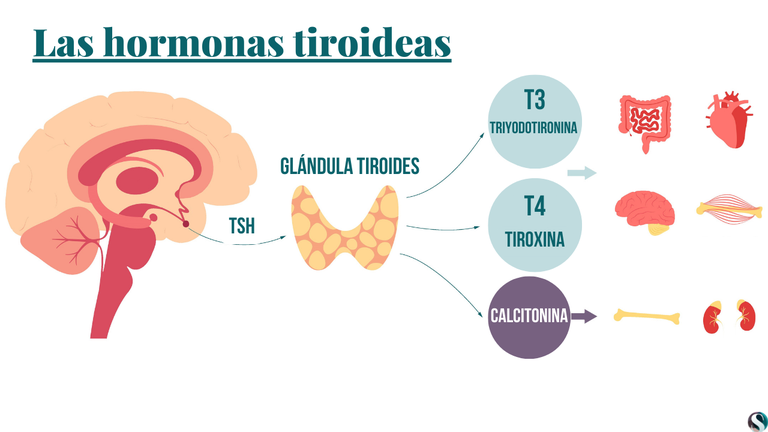
The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system, a network of glands that produce and release hormones to regulate various bodily functions. It weighs less than an ounce but has an outsized impact on your health. The thyroid’s primary function is to produce two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are crucial for regulating metabolism, which is the process by which your body converts food and oxygen into energy. Without proper thyroid function, many bodily processes can be disrupted.
The Production and Regulation of Thyroid Hormones
The production of thyroid hormones is a complex process involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the thyroid itself. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then prompts the thyroid gland to produce T4 and T3. This intricate feedback loop ensures that the body has the right amount of thyroid hormones at all times. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland increase their hormone production to stimulate the thyroid. Conversely, when thyroid hormone levels are high, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland decrease their hormone production to reduce thyroid activity. Understanding this regulation helps in grasping cuál es la función de la tiroides in maintaining hormonal balance.
Key Functions of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones exert a wide range of effects on the body, influencing nearly every organ system. Here are some of the key functions of T4 and T3:
- Metabolism Regulation: Thyroid hormones control the rate at which your body burns calories and uses energy. This affects weight, body temperature, and energy levels.
- Heart Function: Thyroid hormones influence heart rate and the strength of heart contractions. They also help regulate blood pressure.
- Brain Development and Function: Thyroid hormones are crucial for brain development, especially in infants and children. They also affect mood, concentration, and cognitive function in adults.
- Muscle Strength and Function: Thyroid hormones are necessary for maintaining muscle strength and function. They help regulate muscle protein synthesis and breakdown.
- Digestive Function: Thyroid hormones affect the movement of food through the digestive tract and the absorption of nutrients.
- Bone Health: Thyroid hormones play a role in bone remodeling, the process by which old bone is broken down and replaced with new bone.
- Reproductive Health: Thyroid hormones are essential for normal reproductive function in both men and women. They can affect fertility, menstrual cycles, and pregnancy.
These functions clearly illustrate cuál es la función de la tiroides and how critical it is for overall health.
Common Thyroid Disorders
When the thyroid gland doesn’t function properly, it can lead to various disorders. The two most common thyroid disorders are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. This can lead to a slowdown of bodily functions. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, hair loss, and sensitivity to cold. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Other causes include iodine deficiency, thyroid surgery, and radiation therapy.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormones. This can lead to an acceleration of bodily functions. Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, sweating, and tremors. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder, is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Other causes include thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and excessive iodine intake.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders
Diagnosing thyroid disorders typically involves a physical exam, blood tests, and sometimes imaging tests. Blood tests are used to measure TSH, T4, and T3 levels. TSH is usually the first test performed to screen for thyroid disorders. If TSH levels are abnormal, further tests may be needed to determine the specific cause of the problem. Imaging tests, such as thyroid ultrasound or thyroid scan, can help visualize the thyroid gland and identify any abnormalities, such as nodules or inflammation. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you have a thyroid disorder to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding cuál es la función de la tiroides helps in recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely medical attention.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disorders
Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on the specific condition and its severity. Here are some common treatment options:
Treatment for Hypothyroidism
The standard treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone replacement therapy. This involves taking a synthetic form of T4, such as levothyroxine, to replace the hormones that the thyroid gland is not producing. The dosage of levothyroxine is adjusted based on TSH levels to ensure that the body has the right amount of thyroid hormones. Regular monitoring of TSH levels is necessary to maintain optimal thyroid function.
Treatment for Hyperthyroidism
Treatment for hyperthyroidism aims to reduce the production of thyroid hormones. Common treatment options include:
- Antithyroid Medications: These medications, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU), block the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This involves taking radioactive iodine, which destroys thyroid cells and reduces hormone production.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Maintaining Thyroid Health
While some thyroid disorders are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to support thyroid health:
- Ensure Adequate Iodine Intake: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Most people in developed countries get enough iodine from iodized salt and seafood.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and thyroid function.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone balance and thyroid function. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
- Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, can interfere with thyroid function.
- Get Regular Checkups: Regular checkups with your healthcare provider can help detect thyroid disorders early and ensure timely treatment.
The Thyroid and Pregnancy
Thyroid function is particularly important during pregnancy. Thyroid hormones are essential for fetal brain development and growth. Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can lead to complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and developmental problems in the baby. Pregnant women with thyroid disorders require careful monitoring and management to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. Understanding cuál es la función de la tiroides is even more critical during this period.
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps that can develop in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid nodules are benign (noncancerous), but some can be cancerous. Thyroid nodules are often discovered during a routine physical exam or imaging test. If a thyroid nodule is detected, further evaluation may be needed to determine whether it is benign or cancerous. This may involve a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, in which a small sample of cells is taken from the nodule and examined under a microscope. Treatment for thyroid nodules depends on their size, growth rate, and whether they are benign or cancerous.
The Future of Thyroid Research
Ongoing research is focused on improving our understanding of thyroid disorders and developing new and more effective treatments. Areas of research include:
- Genetic Factors: Identifying genes that increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
- Autoimmune Mechanisms: Understanding the role of the immune system in thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
- New Therapies: Developing new medications and therapies for thyroid disorders.
By continuing to investigate the complexities of the thyroid gland, scientists hope to improve the lives of people affected by thyroid disorders. The more we understand cuál es la función de la tiroides, the better equipped we are to treat related ailments.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. Understanding cuál es la función de la tiroides is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can have a significant impact on health and quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing these conditions and preventing complications. By taking steps to support thyroid health, such as ensuring adequate iodine intake and managing stress, you can help keep your thyroid functioning optimally. [See also: Understanding Hypothyroidism Symptoms] [See also: Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options]
